From an IDMF perspective, there are a number of NSW Government initiatives recommended by the State Infrastructure Strategy 2018-2038 that are changing the way that agencies should view spatial and infrastructure data, including:
- Smart Places
- Smart Infrastructure
- Digital Twin
- Digital Engineering
- Internet of Things
- NSW Open Data Portal (Data.NSW).
The primary relationships between these initiatives are illustrated in Figure 3, which highlights the importance of establishing the foundation data layer, including achieving optimal alignment with the higher level initiatives. It holds implications and benefits for all layers of the smart information pyramid as these initiatives will greatly benefit from the adoption of a consistent approach to information and data management.
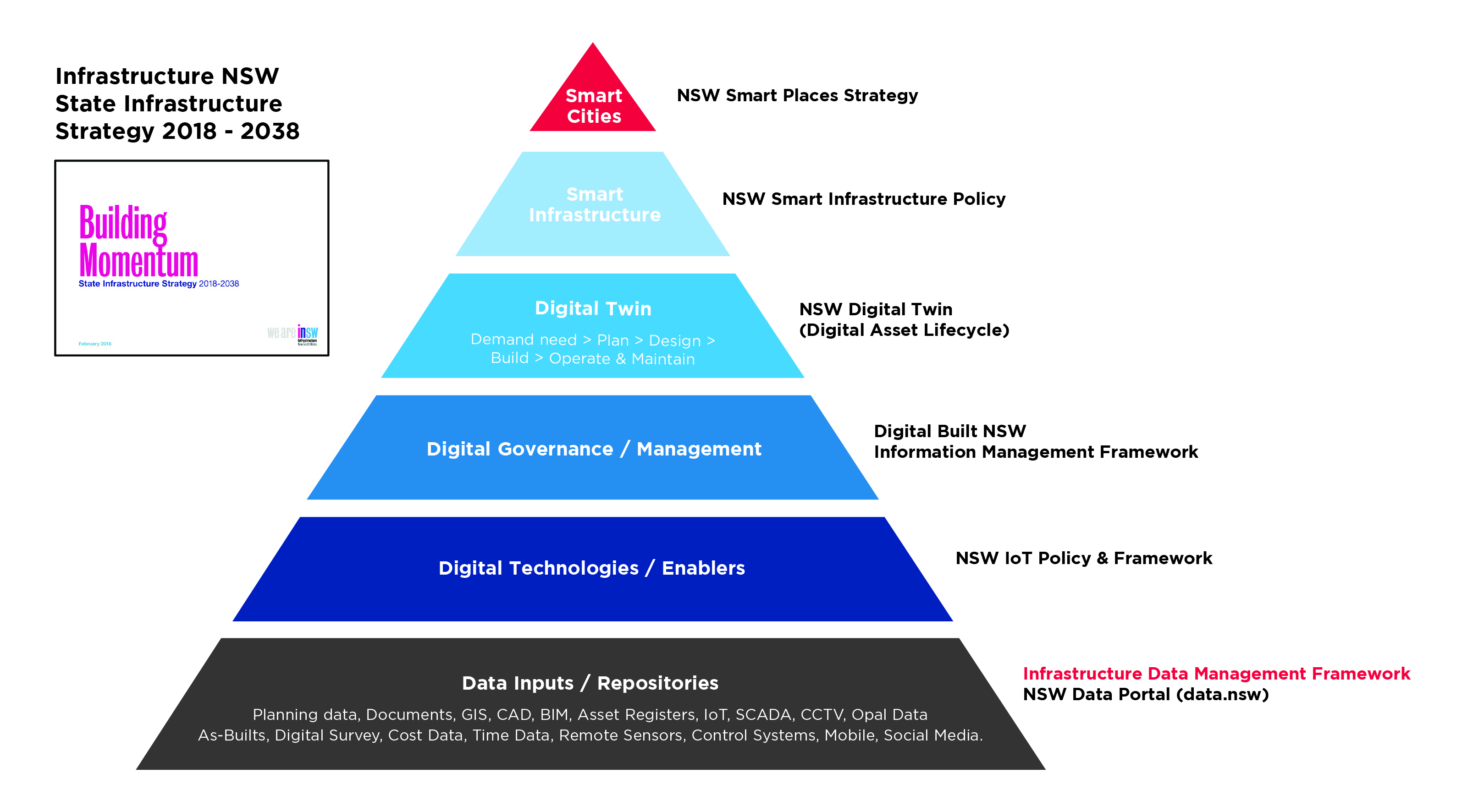
Smart Places and Smart Infrastructure
The NSW Smart Places Strategy provides a vision of the use of technology to collect and use spatially enabled data to make better, evidence-based decisions to improve the productivity, liveability and resilience of cities, towns and communities.
The Smart Places Strategy details an action plan with three focus areas.
- Foundations - Standards and policies to enable consistent implementation and benefits realisation
- Enablers - partnership and procurement improvements
- Programs - new and renewed place transformation and initiatives to drive digital inclusion.
The Smart Places Strategy also outlines the NSW Government’s commitment to providing smart infrastructure that produces, analyses and helps to securely share data, using the best available technologies to capture project, operations and service data.
To assist agencies to embed smart technologies in future infrastructure, the NSW Government has developed the NSW NSW Smart Infrastructure Policy to make sure agencies plan, design, build and operate connected communities, and use infrastructure assets to their full potential. Smart infrastructure will help to realise benefits including improved customer outcomes, productivity improvements, information driven decision making and whole-of-lifecycle asset management.
Digital Twin
A Digital Twin is a digital model of a real-life object, process or system. The digital model can be informed by historical data and fed with live sensor data to make the digital model a ‘twin’ of the real-life, real time subject. Digital Twins of discrete systems can be linked to create twins of larger, more complex systems such as a factory or a city. Figure 4 provides a visual representation of the disparate data layers that can be integrated to provide real time, spatially enabled insights leading to better decisions and better outcomes.
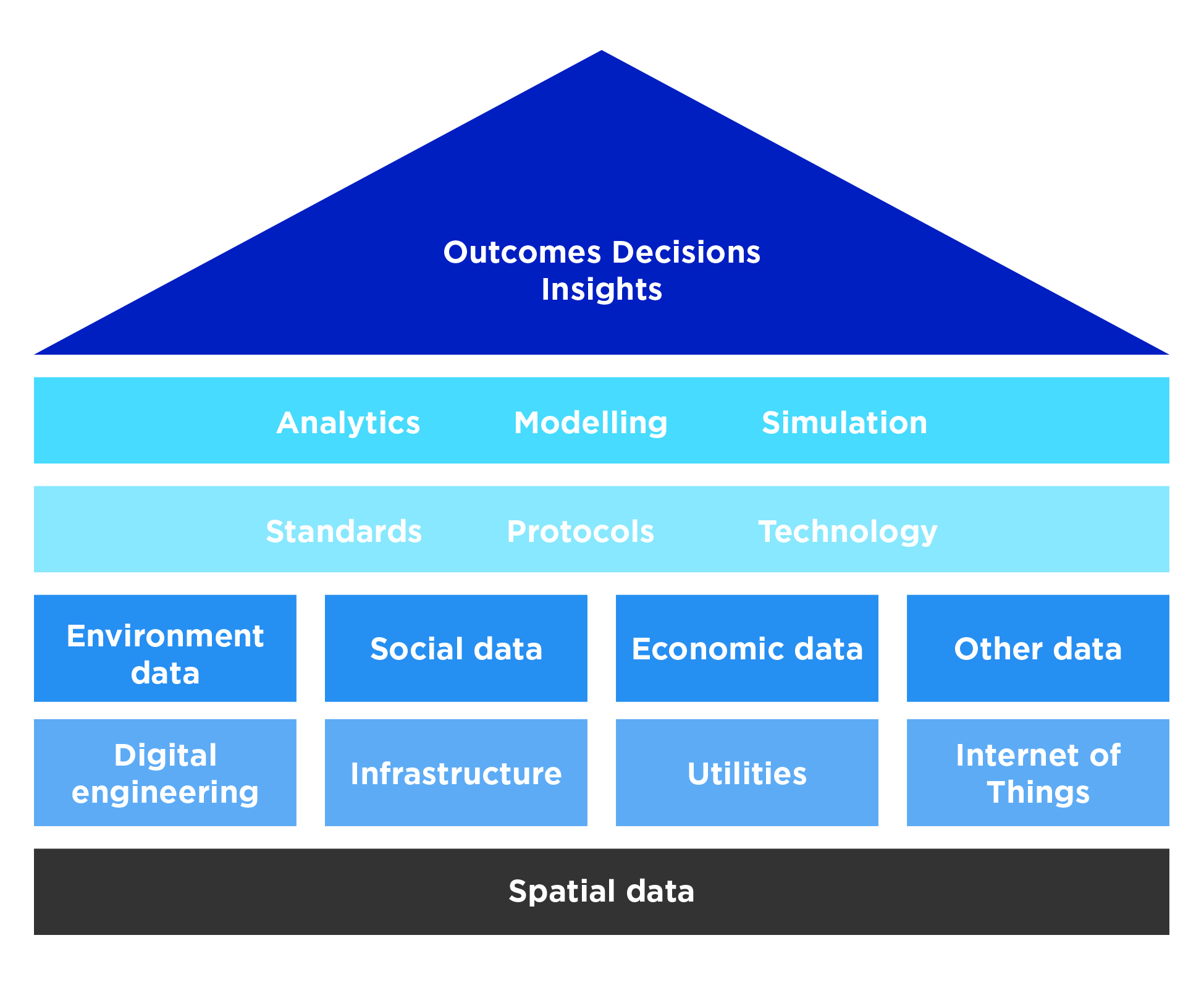
Adapted from the ANZLIC Principles for Spatially Enabled Digital Twins of the Built and Natural Environment in Australia
The NSW Digital Twin is an interactive platform to capture and display real-time 3D and 4D spatial data in order to model the built environment. This is a step change from storing and visualising spatial data in 2D. The NSW ‘Digital Twin’ will help facilitate better planning, design and modelling for future needs. The platform also integrates digital engineering assets, building information models, and live API feeds for public transport, air quality, and energy production. The platform is also designed to integrate with the NSW Spatial Collaboration Portal that provides a central point to search, discover and share spatial information.
The NSW Spatial Collaboration Portal provides a platform for publication and access controlled use of spatially enabled data, and a repository for data to be made available to the Digital Twin viewer. The list of standard data formats that may be used on the Portal are listed at Appendix C – Standards.
Digital Engineering
The National Digital Engineering Policy Principles define Digital Engineering as: the convergence of emerging technologies such as Building Information Modelling (BIM), Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and related systems to derive better business, project and asset management outcomes. Digital Engineering enables a collaborative way of working using digital processes to enable more productive methods of planning, designing, constructing, operating and maintaining assets through their lifecycle.
Digital Engineering activities and systems must also merge with existing asset management practices and integrate with existing Asset Management Systems. The level of maturity of the existing environments must be taken into consideration when developing a 'fit for purpose' enterprise wide system (ecosystem) able to support a range of agencies and their assets.
An action from the NSW Smart Places Strategy is the development of a Digital Built NSW approach with the aim to develop a digital engineering policy, framework and roadmap for NSW. Together with the Asset Management Policy, Digital Built NSW will enable a thriving NSW digital economy for the built environment, encouraging growth and competitiveness and facilitating a more effective use of current and future infrastructure assets.
Last updated 27 Nov 2020